Pathologic nystagmus
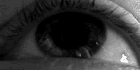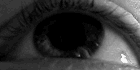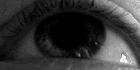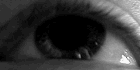 Horizontal optokinetic nystagmus, a normal (physiological) form of nystagmus. |
|
| ICD-10 | H55., H81.4. |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 379.50, 794.14 |
| DiseasesDB | 23470 |
| MeSH | D009759 |
Pathologic nystagmus is a form of involuntary eye movement. It is characterized by alternating smooth pursuit in one direction and saccadic movement in the other direction.
When nystagmus occurs without filling its normal function, it is pathologic (deviating from the healthy or normal condition). Pathological nystagmus is the result of damage to one or more components of the vestibular system, including the semicircular canals, otolith organs, and the vestibulocerebellum.
Pathological nystagmus generally causes a degree of vision impairment, although the severity of such impairment varies widely. Also, many blind people have nystagmus, which is one reason that some wear dark glasses.[1]
Contents |
Prevalence
Nystagmus is a relatively common clinical condition, affecting one in every 5,000 to 10,000 individuals. One survey in Oxfordshire, England, reported that one in every 670 children has manifesting nystagmus by the age of two.[2] Authors of another study in the United Kingdom estimated an incidence of 24 in 10,000, noting an apparently higher rate amongst white Europeans than in individuals of Asian origin.[3]
Variations
- Peripheral nystagmus occurs as a result of either normal or diseased functional states of the vestibular system and may combine a rotational component with vertical or horizontal eye movements and may be spontaneous, positional, or evoked.
- Positional nystagmus occurs when a person's head is in a specific position.[4] An example of disease state in which this occurs is Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
- Gaze Induced nystagmus occurs or is exacerbated as a result of changing one's gaze toward or away from a particular side which has an affected vestibular apparatus.
- Post rotational nystagmus occurs after an imbalance is created between a normal side and a diseased side by stimulation of the vestibular system by rapid shaking or rotation of the head.
- Spontaneous nystagmus is nystagmus that occurs randomly, regardless of the position of the patient's head.
- Central nystagmus occurs as a result of either normal or abnormal processes not related to the vestibular organ. For example, lesions of the midbrain or cerebellum can result in up- and down-beat nystagmus.
Causes
The cause for pathological nystagmus may be congenital, idiopathic, or secondary to a pre-existing neurological disorder. It also may be induced temporarily by disorientation (such as on roller coaster rides) or by certain drugs (alcohol and other central nervous system depressants, inhalant drugs, and the dis-associative anesthetics [PCP]).
Congenital
Congenital nystagmus occurs more frequently than acquired nystagmus. It can be insular or accompany other disorders (such as micro-ophthalmic anomalies or Down's Syndrome). Congenital nystagmus itself is usually mild and non-progressive. The affected persons are not normally aware of their spontaneous eye movements, but vision can be impaired depending on the severity of the movements.
Types of congenital nystagmus include the following:
- Infantile:
-
- Idiopathic
- Albinism
- Aniridia
- Leber's congenital amaurosis
- Bilateral optic nerve hypoplasia
- Bilateral congenital cataracts
- Rod monochromatism
- Optic nerve or macular disease
- Persistent tunica vasculosa lentis
- Visuo-motor syndrome of functional monophthalmos
- Noonan syndrome
- Latent nystagmus
- Nystagmus blockage syndrome
X-linked infantile nystagmus is associated with mutations of the gene FRMD7, which is located on the X chromosome.[5][6]
Congenital nystagmus is also associated with two X-linked eye diseases known as complete congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB) and incomplete CSNB (iCSNB or CSNB-2), which are caused by mutations of one of two genes located on the X chromosome. In CSNB, mutations are found in NYX (nyctalopin).[7][8] CSNB-2 involves mutations of CACNA1F, a voltage-gated calcium channel that, when mutated, does not conduct ions.[9]
Acquired
Diseases
Some of the diseases that present nystagmus as a pathological sign:
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo [10]
- Head trauma
- Stroke (the most common cause in older people)
- Ménière's disease and other balance disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain tumors
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
- Encephalopathy
- Lateral medullary syndrome
- Aniridia
- Optic nerve hypoplasia
- Albinism
- Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease
- Superior canal dehiscence syndrome
- Tullio phenomenon
- Horner's Syndrome
- Whipple's disease
Toxic/metabolic
Nystagmus from toxic or metabolic reasons could be the result of the following:
- Alcohol intoxication
- Lithium
- Barbiturates
- SSRIs
- Phenytoin (Dilantin)
- Salicylates
- Benzodiazepines
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Ketamine
- Other anticonvulsants or sedatives
- Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
- Wernicke's encephalopathy
- Thiamine deficiency
Central nervous system disorders
If the pathologic nystagmus is based in the central nervous system (CNS), such as with a cerebellar problem, the nystagmus can be in any direction including horizontal. Purely vertical nystagmus is usually central in origin.
Causes include e.g.:
- Thalamic hemorrhage
- Tumor
- Stroke
- Trauma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Withdrawal from certain antidepressants[11]
Other causes
- Vestibular Pathology (Ménière's disease, SCDS (superior canal dehiscence syndrome), BPPV, Labyrinthitis)
- Trochlear nerve malfunction[12]
- Non-physiologic
Diagnosis
Nystagmus is very noticeable but little recognized. Nystagmus can be clinically investigated by using a number of non-invasive standard tests. The simplest one is Caloric reflex test, in which one external auditory meatus is irrigated with warm or cold water. The temperature gradient provokes the stimulation of the vestibulocochlear nerve and the consequent nystagmus.
The resulting movement of the eyes may be recorded and quantified by special devices called electronystagmograph (ENG), a form of electrooculography (an electrical method of measuring eye movements using external electrodes),[13] or even less invasive devices called videonystagmograph (VNG),[14] a form of video-oculography (VOG) (a video-based method of measuring eye movements using external small cameras built into head masks) by an audiologist. Special swinging chairs with electrical controls are also used in this test to induce rotatory nystagmus.[15]
Treatment
Congenital nystagmus has traditionally been viewed as non-treatable, but medications have been discovered in recent years that show promise in some patients. In 1980, researchers discovered that a drug called baclofen could effectively stop periodic alternating nystagmus. Subsequently, gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, was found to cause improvement in about half the patients who received it to relieve symptoms of nystagmus. Other drugs found to be effective against nystagmus in some patients include memantine[16], levetiracetam, 3,4-diaminopyridine, 4-aminopyridine, and acetazolamide.[17] Several therapeutic approaches, such as contact lenses,[18] drugs, surgery, and low vision rehabilitation have also been proposed.
Clinical trials of a surgery to treat nystagmus (known as tenotomy) concluded in 2001. Tenotomy is being performed regularly at the University of Pittsburgh Children's Hospital and by a handful of surgeons around the world. The surgery developed by Louis F. Dell'Osso Ph.D aims to reduce the eye shaking (oscillations), which in turn tends to improve visual acuity.
Research
Several universities are researching nystagmus and are looking for volunteers to take part in research activities.
See also
- Opsoclonus
- Optokinetic nystagmus
- Orthoptist
- Physiologic nystagmus
References
- ↑ "nystagmus". http://www.drhull.com/EncyMaster/N/nystagmus.html. Retrieved 2007-06-07.
- ↑ "American Nystagmus Network-About Nystagmus". http://www.nystagmus.org/aboutn.html. Retrieved 2007-06-07.
- ↑ PMID 19458336 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Anagnostou E, Mandellos D, Limbitaki G, Papadimitriou A, Anastasopoulos D (June 2006). "Positional nystagmus and vertigo due to a solitary brachium conjunctivum plaque". J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 77 (6): 790–2. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2005.084624. PMID 16705203. PMC 2077463. http://jnnp.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16705203.
- ↑ PMID 18161616 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Li N, Wang L, Cui L, et al. (2008). "Five novel mutations of the FRMD7 gene in Chinese families with X-linked infantile nystagmus". Mol. Vis. 14: 733–8. PMID 18431453.
- ↑ PMID 16157331 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 18617546 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 17949918 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Dorigueto RS, Ganança MM, Ganança FF (2005). "The number of procedures required to eliminate positioning nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo". Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol (Engl Ed) 71 (6): 769–75. PMID 16878247. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992005000600014&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en.
- ↑ Christmas, David M. B. "‘Brain shivers’: from chat room to clinic ". The Psychiatrist (2005) 29: 219-221. doi: 10.1192/pb.29.6.219
- ↑ Lindgren, Stefan (1993) (in Swedish). Kliniska färdigheter: Informationsutbytet mellan patient och läkare. Lund: Studentlitteratur. ISBN 91-44-37271-X.
- ↑ PMID 17982846 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 14526552 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ PMID 17314477 (PubMed)
Citation will be completed automatically in a few minutes. Jump the queue or expand by hand - ↑ Memantine/Gabapentin for the treatment of congenital nystagmus. PMID: 17764629
- ↑ Groves, Nancy. Many options to treat nystagmus, more in development. Ophthalmology Times, March 15, 2006. [1]
- ↑ Biousse V, Tusa RJ, Russell B, et al. (February 2004). "The use of contact lenses to treat visually symptomatic congenital nystagmus". J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 75 (2): 314–6. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.010678. PMID 14742616. PMC 1738913. http://jnnp.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14742616.
External links
- American Nystagmus Network — US-based support organisation
- Nystagmus Network UK — UK-based support organisation
- nystagmus.co.uk — a teenager's experiences of nystagmus and a friendly forum
- The Shifty Eyes Blog — a blog about life with nystagmus
- Nystagmus Blog — A blog about Nystagmus, A parent’s perspective
- GeneReview/NIH/UW entry on FRMD7-Related Infantile Nystagmus
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||